The Traffic Act explains how roads should be used and how road users are expected to behave.
It also outlines the penalties or fines for breaking the law.
THE HIGHWAY CODE
The Highway Code is a comprehensive guide that provides rules, advice, and guidance for all road users in Kenya.
Its purpose is to promote safety, good behavior, and courtesy on the roads.

Key points covered in the Highway Code include:
Rules for drivers: Proper driving techniques, obeying speed limits, lane discipline, and safe overtaking.
Rules for pedestrians: Safe road crossing, using sidewalks, and respecting traffic signals.
Rules for cyclists and motorcyclists: Helmet use, lane positioning, signaling, and visibility.
Traffic signs and road markings: Understanding warning, regulatory, and informative signs.
Behavior and attitude: Encouraging courteous and responsible conduct on the road.
Emergency situations: Procedures for collisions, breakdowns, and giving way to emergency vehicles.
Reading and following the Highway Code is essential for all road users to ensure safety, prevent accidents, and promote a respectful traffic environment.
LEARNING ROAD RULES
Read the Traffic Act and the Highway Code to learn the rules for safe driving.
Focus on safety, courtesy, and responsibility while using the road.

KEY TRAFFIC RULES
Speed limits – Driving within the legal and safe speed for the road and conditions.
Lane discipline – Staying in your lane and using proper lane-changing signals.
Right of way – Understanding who has priority at junctions, pedestrian crossings, and roundabouts.
Traffic signs and signals – Obeying warning, regulatory, and informative signs as well as traffic lights.
Use of horn – Using the horn responsibly and only when necessary.
Emergency vehicles – Giving way to ambulances, fire engines, police, and other authorized vehicles.
Pedestrian and cyclist safety – Avoiding areas designated for pedestrians or cyclists.
Seat belts and safety measures – Ensuring all occupants are secured and following safe driving practices.

USING THE HORN
Use the horn only, when necessary, such as while moving or to warn others of your presence.
Do not honk when your vehicle is stationary.
Avoid aggressive honking, even if other road users are at fault.
Respect ‘No Hooting’ areas, such as hospitals, schools, and other sensitive zones.

Give way to emergency vehicles such as police cars, fire engines, ambulances, and the presidential motorcade.
Follow instructions from police officers, traffic marshals, or other authorized personnel promptly and safely.
Do not drive or ride in areas designated for pedestrians or cyclists.
Always stay in your appropriate lane or roadway to ensure the safety of others.


TRAFFIC SIGNS AND SIGNALS
Traffic Signals communicate instructions to road users to ensure safe and orderly movement.
There are two main types of signals:
Hand Signals – Given by police officers or traffic marshals to control traffic manually.

Light Signals – Traffic lights that indicate when to stop, go, or proceed with caution.

Traffic Signs guide, warn, and provide information to road users.
The main types of signs include:
Triangle – Warning

Circle – Regulatory signs giving orders or instructions that must be obeyed.

Rectangle – Informational signs providing directions or general information.

ONE WAY TRAFFIC ROAD
A one-way traffic road is a road, usually with two or more lanes, where all vehicles move in the same direction.
The road is divided into lanes by white broken or continuous lines, and sometimes by a pavement or median at the center.
On a one-way road, drivers may change lanes, but overtaking is not allowed, even though it may appear similar to overtaking.

LANE MARKINGS
White continuous line: You must not change lanes. Maintain your position and stay within your lane.
White broken line: You may change lanes in your chosen direction, but only when the road is clear.
Change lanes carefully and at your own risk.
LANE CHANGING TECHNIQUE (M.S.M)
M – Mirror: Check your mirrors to ensure it is safe to move.
S – Signal / Indicate: Show your intention to change lanes using the indicator.
M – Maneuver: Move smoothly


ROAD COMMUNICATION AND MSM TECHNIQUE
Road users communicate through hand signals, indicator lights, and instructions from traffic officers to prevent accidents and maintain smooth traffic flow.
MSM Technique (Mirror, Signal, Manoeuvre):
Use this routine every time you:
Move off (start driving from a stopped position).
Turn, change lanes, or overtake another vehicle.
Change speed, either when slowing down or speeding up.
MIRROR
Check your interior and side mirrors
Look for hazards such as vehicles behind you, fast approaching cars, cyclists, and motorcyclists.
Adjust your speed if another vehicle is following too closely.
Always check your blind spots before:
- Changing lanes
- Overtaking
- Changing direction where hazards might be hidden

SIGNAL
Signal clearly in the direction you intend to go.
Always check your mirrors before applying any signal.
Signal in good time, not too early or too late, to avoid confusing other road users.

MANOEUVRING
Use the manoeuvre phase when turning, parking, changing lanes, or approaching roundabouts.
Be prepared to adjust your MSM routine if new hazards appear.
Anticipate and predict possible dangers from pedestrians, cyclists, or other vehicles, and react safely.
HAND SIGNALS BY DRIVERS
Turn left / Move left: Extend your left hand straight out.

Turn right / Move right: Bend your left arm upward, or extend your right hand if local regulations allow.

Slow down / Stop: Bend your left arm downward.

HAND SIGNALS BY DRIVERS TO TRAFFIC POLICE
Move left: Signal with your left hand

Move right: Signal with your right hand

Go straight: Signal by holding your hand straight ahead.

LIGHT SIGNALS BY VEHICLES
Turn Turn: Switch on the left indicator.

Right Turn: Switch on the right indicator.

Braking / Slowing Down: Brake lights illuminate automatically.

Reversing / Backing Up: Reverse lights turn on automatically.

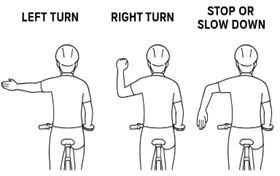
HAND SIGNALS BY MOTORCYCLISTS
Turn left / Move left: Extend your left arm straight out.
Turn right / Move right: Bend your left arm upward.
Slow down / Stop: Bend your left arm downward.
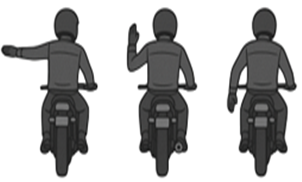
HAND SIGNALS BY CYCLISTS
Turn Left: Extend your left arm straight out.
Turn Right: Bend your left arm upward.
Slow Down / Stop: Bend your left arm downward.
HAND SIGNALS BY TRAFFIC POLICE OFFICERS
Stop traffic from both directions: Arms raised horizontally.

Stop traffic from behind: Arm pointing backward.

Move / Come forward: Arm waving forward.

Stop traffic from the front: Arm pointing forward.

SIGNALS BY TRAFFIC MARSHALS
Barrier to stop pedestrians: Use a stop sign or barrier.

Pedestrians ready to cross: Prepare to stop vehicles.

All vehicles must stop: Raised hand or flag

Pedestrians not ready to cross: Keep vehicles moving.

TRAFFIC LIGHT SIGNALS
Green Arrow: You may move in the direction shown if the road is clear.

Signal Blackout / Lights Not Working:

Stop at the intersection.
Proceed only when all other vehicles, bicycles, and pedestrians have stopped.
TWO WAY TRAFFIC ROAD (SINGLE CARRIAGE)
A two-way traffic road has two lanes, with a single lane for each direction, where traffic moves in opposite directions.
The road is divided by single or double yellow lines, which may be continuous or broken.
On this road, overtaking is allowed. (Overtaking means temporarily moving into the opposite lane to pass a slower vehicle, then returning to your lane.)

LANE MARKINGS AND OVERTAKING RULES
Yellow Continuous Line: Do not overtake at this point.
Yellow Broken Line: You may overtake a slow-moving vehicle, but only when the opposite lane is clear.
Double Continuous Yellow Line: Overtaking is not allowed for vehicles in either lane.
Double Line (Continuous + Broken): The vehicle on the broken line side may overtake, while the vehicle on the continuous line side must not overtake.



